1-dimension array 1 2 3 4 int [] arr = new int []{ 1 , 2 , 3 };int [] arr2 = {1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 };int len = arr.length; int len2 = arr2.length;
2-dimension array 1 int [][] matrix = {{1 , 2 }, {3 , 4 }};
Linklist object 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {} ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } }
String 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 String str = "hello" ;int len = str.length(); Char c = str.charAt(0 ); "String" .substring(int beginIndexInclusive, int endIndexExclusive);"T" .repeat(3 );
Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 Integer.toBinaryString(15 ) Integer.parseInt("1111" , 2 ) BigInteger n = BigInteger.ONE;n.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(123 )); n.divide(BigInteger.valueOf(123 ));
Angle could be measured in degrees or radians.atan stands for “arc tangent.” It is the inverse function of tangent - this means it undoes the tangent function. So atan(tan(30)) = 30.
atan(delta-y/delta-x) == atan2(delta-y, delta-x) // be mindful delta x could be zeroMath.atan(1) == Math.PI / 4.0 == Math.atan2(1, 1)
StringBuilder 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ("String" );sb.append("String" ); sb.insert(0 , Integer.toString(123 )); sb.insert(3 , "s" ); sb.deleteCharAt(4 ); sb.setCharAt(9 , 's' ); sb.reverse(); sb.toString();
Two ways to copy string 1 2 3 String original = "Original" ;String copiedString1 = String.valueOf(original);String copiedString2 = new StringBuilder (original).toString();
1 2 3 4 String sentence = "Hello world hello again" ;List<String> splits = Arrays.asList(sentence.split("\\s+" )); Collections.reverse(splits); String.join(" " , splits);
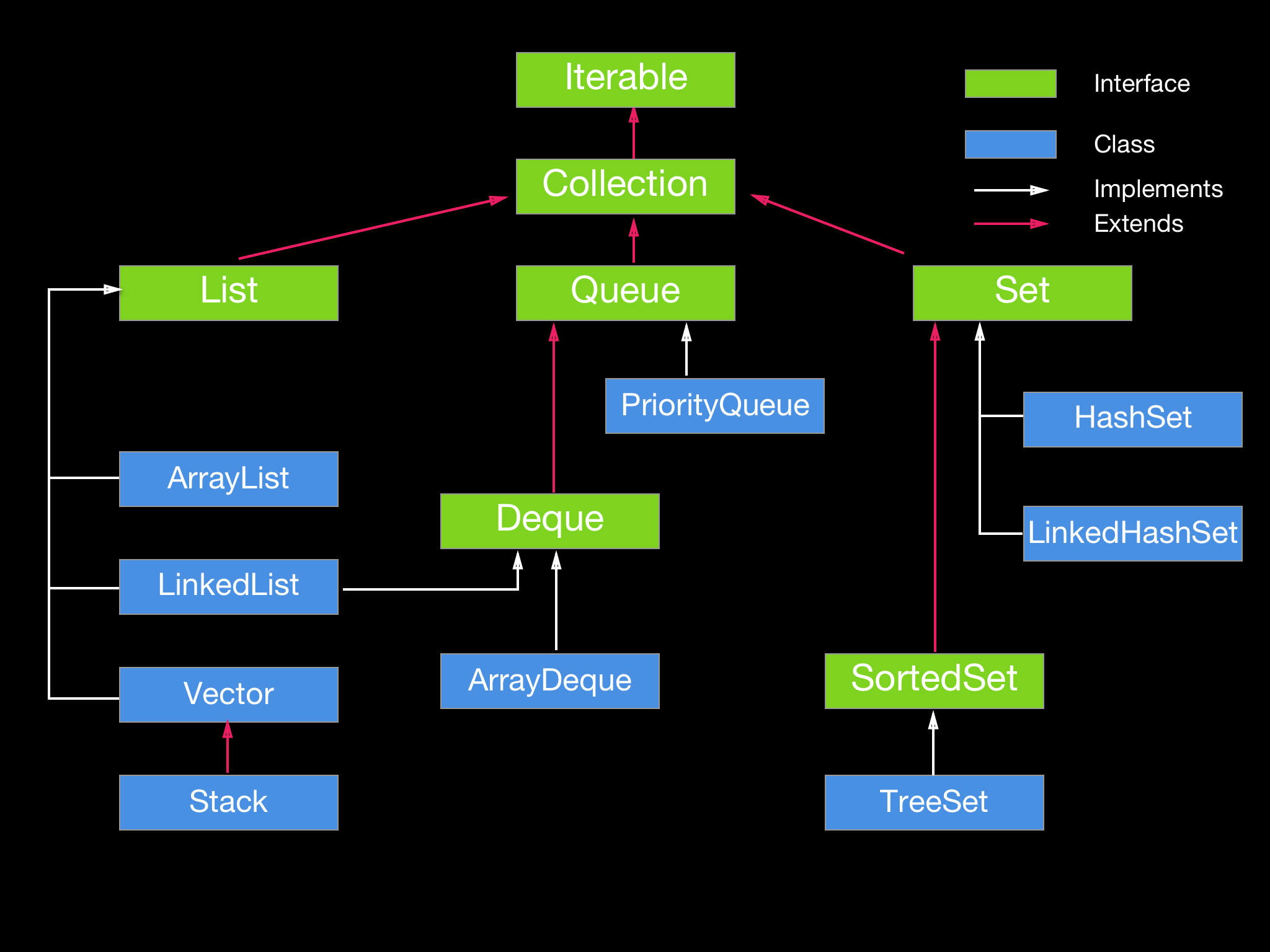
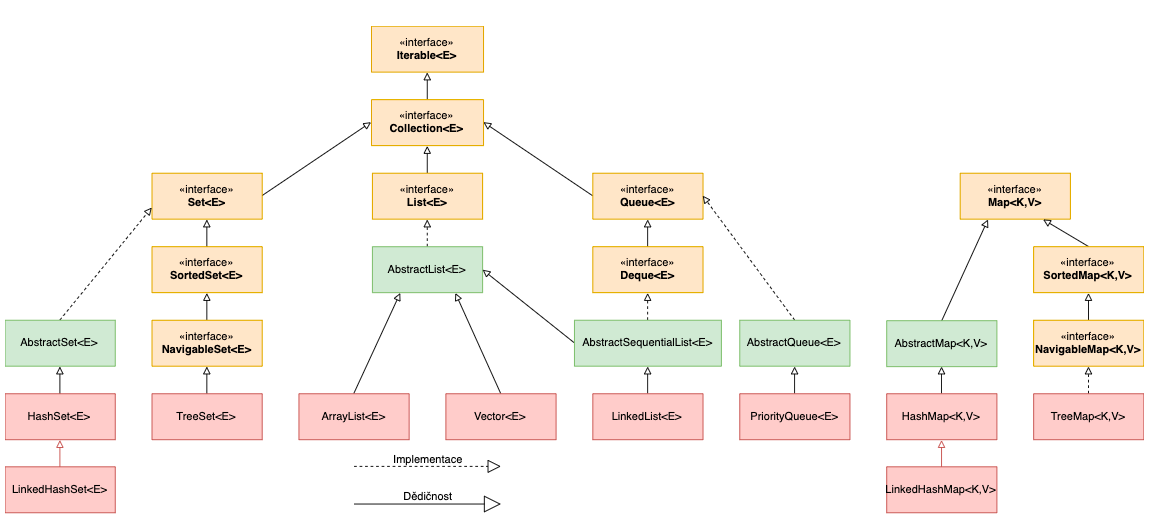
Containers
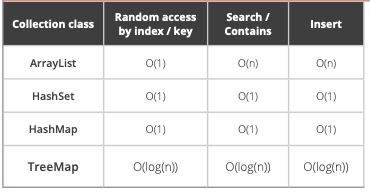
List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 List<Integer> list = new LinkedList <>(); list.add(1 ); list.size(); List<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList <>(List.of(1 , 3 , 5 )); list2.contains(1 ); list2.get(2 ); list2.remove(1 ); List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList(1 , 5 , 9 , 11 )); list3.isEmpty(); list3.remove(0 );
Vectors are synchronized, ArrayLists are not.
Array / List conversion 1 2 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("C" , "C++" , "Java" ); String[] array = list.toArray();
Copy LinkedList 1 2 3 4 5 LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList <>(); list.add("test" ); List<Integer> clonedList = new LinkedList <Integer>(); clonedList = (LinkedList) list.clone();
Stack 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Stack<Integer> st = new Stack <>(); st.push(1 ); st.push(2 ); st.push(3 ); Integer top = st.pop(); Integer peekTop = st.peek(); st.isEmpty(); Integer pos = st.search(1 ); Integer pos2 = st.search(2 ); Integer pos3 = st.search(3 );
Queue 1 2 3 4 5 6 Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList <>(); q.add(1 ); q.add(2 ); q.add(3 ); q.isEmpty(); Integer top = q.poll(); Integer peekTop = q.peek();
Deque 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.add(1 ); deque.addLast(2 ); deque.addFirst(3 ); deque.peekFirst(); deque.peekLast(); deque.size(); deque.removeFirst(); deque.removeLast();
Heap / Priority queue 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue (); pq.addAll(List.of(3 ,5 ,7 ,9 ,11 ,1 )); int top = pq.poll(); int peekTop = pq.peek(); pq.isEmpty(); pq.remove(7 ); int size = pq.size(); PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue (Comparator.reverseOrder()); pq.addAll(List.of(3 ,5 ,7 ,9 ,11 ,1 )); int top = pq.poll(); int peekTop = pq.peek(); pq.isEmpty(); pq.remove(7 ); int size = pq.size(); PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue <String>(Collections.reverseOrder(Comparator.comparing(String::length));
HashSet HashMap HashTable
HashTables are synchronized, HashMaps are not.
HashSet is unordered and unsorted Set. LinkedHashSet is the ordered version of HashSet, LinkedHashSet maintains the insertion order. When we iterate through a HashSet, the order is unpredictable while it is predictable in case of LinkedHashSet.
HashSet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); set.add(1 ); set.add(3 ); set.add(9 ); set.isEmpty(); set.contains(9 ); for (Object num : set) {}new ArrayList (set);
HashMap:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put(1 ,2 ); map.put(3 ,4 ); map.put(5 ,6 ); map.put(7 ,8 ); map.containsKey(1 ); map.containsKey(2 ); map.put(1 , 10 ); map.get(1 ); map.get(10 ); map.computeIfAbsent(9 , k -> new LinkedList <>()); map.getOrDefault(9 , new LinkedList <>());
TreeSet 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet <>(); set.add(1 ); set.add(3 ); set.add(5 ); set.add(7 ); set.ceiling(2 ); set.ceiling(3 ); set.floor(2 ); set.floor(3 ); set.lower(2 ); set.lower(3 ); set.higher(2 ); set.higher(3 );
TreeMap Under the hood, it is implemented by a red-black tree structure.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap (); map.put(1 , 11 ); map.put(2 , 22 ); map.put(5 , 55 ); map.put(3 , 33 ); Integer v = map.get(3 ); Integer v2 = map.get(8 ); boolean c1 = map.containsKey(3 ); boolean c2 = map.containsValue(22 ); Integer first = map.firstKey(); Integer last = map.lastKey(); map.remove(1 ); Integer first2 = map.firstKey(); map.ceilingKey(4 ); map.ceilingKey(5 ); map.floorKey(4 ); map.higherKey(4 ); map.higherKey(5 ); map.lowerKey(4 ); map.get(1 ); map.get(8 );
Sort Sort array 1 2 3 Integer[] arr = { 13 , 7 , 6 , 45 , 21 }; Arrays.sort(arr); Arrays.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
Sort collection 1 2 3 List<Integer> list = new LinkedList <>(List.of(3 , 1 , 2 , 8 , 7 )); Collections.sort(list); Collections.sort(list, Collections.reverseOrder());
Custom comparator 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class TestClass { int sortKey; String otherProps; public TestClass (int k, String v) { sortKey = k; otherProps = v; } } class SortByKey implements Comparator <TestClass> { @Override public int compare (TestClass t1, TestClass t2) { if (t1.sortKey < t2.sortKey) { return -1 ; } else if (t1.sortKey == t2.sortKey) { return 0 ; } else { return 1 ; } } } List<TestClass> list = new LinkedList <>(List.of( new TestClass ( 1 , "a" ), new TestClass ( 8 , "ddd" ), new TestClass ( 3 , "aaa" ), new TestClass ( 11 , "cc" ), new TestClass ( 6 , "b" ) )); Collections.sort(list, new SortByKey ());
Another way to implement, which might be easier
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class TestClass implements Comparable <TestClass> { int sortKey; String otherProps; public TestClass (int k, String v) { sortKey = k; otherProps = v; } @Override public int compareTo (TestClass o) { return Integer.compare(sortKey, o.sortKey); } }
Java stream 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 List<String> fromList = Arrays.asList("zza" , "bb" , "ccc" , "dddd" ); List<String> result = fromList.stream() .filter((item) -> item.length() > 0 ) .sorted((s1, s2) -> s1.charAt(0 ) - s2.charAt(0 )) .map(s -> s.replace("a" , "A" )) .collect(Collectors.toList()); Optional<String> reducedResult = result.stream() .reduce((s1, s2) -> String.format("%s:%s" , s1, s2)); String[] fromArray = {"a" , "b" , "c" }; long count = Arrays.stream(fromArray).count();
Java IO Byte Streams, file content: test
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 try ( InputStream fis = new FileInputStream (filePathInput); OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream (filePathOutput) ) { int content; while ((content = fis.read()) != -1 ) { System.out.print((char ) content); System.out.print("," ); } fos.write("hello" .getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { }
I/O operations are very performance-intensive. Buffered streams load data into a buffer and read/write multiple bytes at once, thereby avoiding frequent I/O operations and improving the efficiency of stream transmission.
Byte buffered streams use the decorator pattern to enhance the functionality of the InputStream and OutputStream
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader (new FileReader (filePathInput)); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter (new FileWriter (filePathOutput))) { String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null ) { writer.write(line); writer.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { }
Character streams use Unicode encoding by default, but we can customize the encoding through the constructor.
UTF-8: English characters: 1 byte, Chinese characters: 3 bytes.
Unicode: Any character: 2 bytes.
GBK: English characters: 1 byte, Chinese characters: 2 bytes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader (filePathInput, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);) { int content; while ((content = fileReader.read()) != -1 ) { System.out.print((char ) content); } } catch (IOException e) { }